PRESS RELEASE
Kirin and Fujitsu elucidate a novel gut-brain axis mechanism of citicoline for the first time worldwide through AI-based analysis and experimental validation leveraging drug discovery DX technology
Kirin Holdings Company, Limited
Fujitu Limited
Tokyo and Kawasaki, December 17, 2025
Kirin Holdings Company, Limited and Fujitsu Limited have jointly conducted research on food functionality simulation with the goal of creating new functionalities in food. This research utilized QSP (Quantitative Systems Pharmacology) models[1], one of the AI-driven digital transformation (DX) technologies for drug discovery[2], combined with real-world experimental validation. As a result, the study has, for the first time worldwide, identified a previously unknown mechanism within the gut-brain axis[3] associated with citicoline[4], a compound known for its role in supporting cognitive health. This finding was obtained by combining virtual subject simulations based on advanced QSP technologies developed by Fujitsu in collaboration with its partner Nova In Silico SAS(France) with cell-based experimental validation.
Conventional drug discovery has been time-consuming and costly, with limitations in improving confidence in demonstrating efficacy in humans. In recent years, the diversification of medical needs and stricter constraints on animal testing have further increased the demand for efficient R&D. To address these challenges, the introduction of DX technologies utilizing AI and data science has been accelerating. In particular, virtual subject generation and in silico simulation[5] enabled by DX technologies are expected to improve reliability in demonstrating efficacy in humans without animal testing, making their application in food functionality research highly promising.
This study represents a globally pioneering example of the full-scale application of DX technologies in food functionality research. It evaluated novel physiological functions of citicoline by combining AI-based prediction with experimental validation. These findings are expected to accelerate the adoption of AI-driven DX technologies in health science and contribute significantly to realizing a society that promotes longevity and well-being through innovative food solutions.
Research Results
We collected information on citicoline’s metabolic profile and its action-related receptors from Kirin’s proprietary data and literature reviews. Using digital transformation (DX) technology, we constructed a QSP model to evaluate the functional properties of citicoline. Simulations using this model predicted that oral administration of citicoline enhances cholinergic signaling in the gut–nerve axis (Figure 1) and induces a dose-dependent increase in acetylcholine levels within intestinal synapses (Figure 2). In parallel, in vitro experimental validation confirmed that citicoline activates neuronal signaling through the intestinal pathway in a co-culture system of intestinal epithelial cells and neurons (Figure 3).
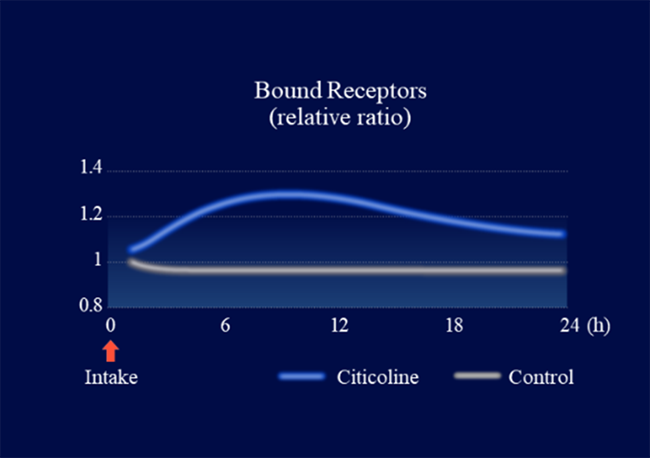
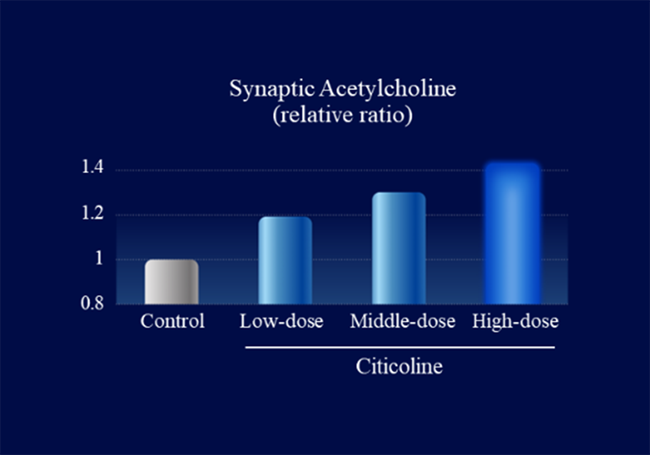
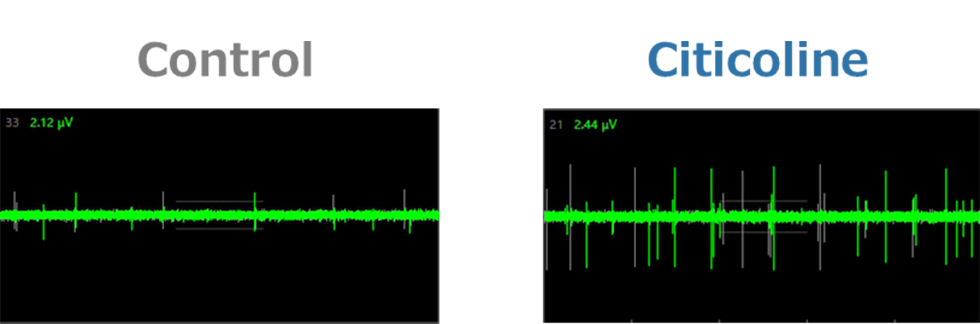
Key Findings
This study predicted, through AI-based analysis, that citicoline could activate neuronal signaling via the gut and validated this prediction in vitro. Furthermore, gut nerves are known to be closely interconnected with the brain. This research has elucidated part of the gut-brain mechanism of citicoline.
Future Plans
This study represents a globally pioneering example of the full-scale application of DX technology in food functionality research. It provides insights that help elucidate new physiological functions of citicoline, which are essential for supporting brain function, thereby enhancing citicoline’s value as a functional ingredient for health.
Note
-
[1] QSP (Quantitative Systems Pharmacology) models:
An information science approach that integrates physiological and pathophysiological networks into computational models to predict drug activity, therapeutic effects, and systemic effects of nutrients.
-
[2] AI-driven digital transformation (DX) technologies for drug discovery:
A method that uses digital technologies such as AI to comprehensively elucidate interactions between disease-related biological systems and drug discovery candidates, including pharmacokinetics and side effects, through mathematical modeling and computer-based analysis. This approach enables the analysis of large-scale molecular data and efficient identification of new drug candidates.
-
[3] Gut-brain axis:
A bidirectional communication network in which the gut and brain influence each other, interconnected through neural, endocrine, immune, and metabolic pathways.
-
[4] Citicoline:
A compound manufactured by Kyowa Hakko Bio, part of the Kirin Group, and marketed globally since the early 1990s, primarily in Europe and the United States. It is widely used as an ingredient in supplements and beverages designed to support cognitive function, as well as in pharmaceutical formulations. Currently, citicoline is approved for pharmaceutical use only in Japan.
-
[5] In silico simulation:
An information science methodology that uses data analysis of biological phenomena to predict biological and pharmacological processes and functionalities through computer-based simulations.
Press Contacts
Kirin Holdings Company, Limited
Corporate Communication Department
Nakano Central Park South, 4-10-2 Nakano, Nakano-ku, Tokyo
+81-3-6837-7028
Fujitsu Limited
Public and Investor Relations Division
All company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 17 December, 2025
City: Tokyo and Kawasaki, Japan
Company: Kirin Holdings Company, Limited, Fujitsu Limited
