Quantum Computing
The Quantum R&D Division at Fujitsu Research of India Pvt Ltd (FRIPL) combines the strengths of Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing to build next-generation computational systems. As part of a global network of Fujitsu Quantum Labs across Japan, India, the USA, and Europe, the India team contributes to the complete Quantum Computing Stack, spanning hardware, simulators, algorithms, and applications.
Aligned with Fujitsu’s purpose of making the world more sustainable by building trust through innovation, FRIPL’s Quantum Lab is developing scalable quantum solutions that aim to transform industries and scientific discovery.
Quantum Algorithm Development
FRIPL focuses on creating quantum algorithms that are not only theoretically powerful but also practically applicable using Fujitsu’s quantum hardware and simulators. Areas of focus include:
- Variational Quantum Algorithms (VQAs) for use in optimization, quantum chemistry, and simulation
- Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation (FTQC) algorithms for complex problems like database search and prime factorization
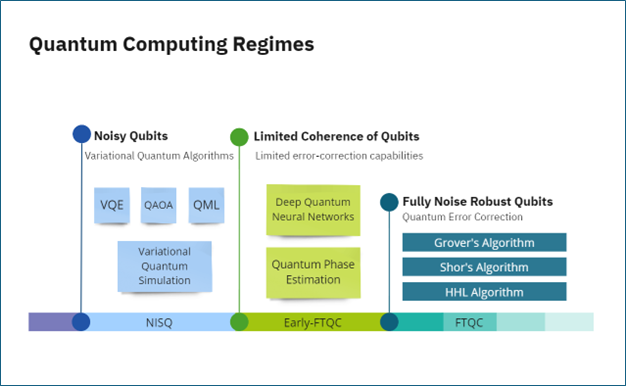
While many quantum algorithms promise exponential speedups, most require a large number of qubits and high circuit depth. FRIPL is actively exploring hybrid quantum-classical algorithms that can function within the limitations of current Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices to deliver near-term advantage.
Quantum Machine Learning
Quantum Machine Learning (QML) merges quantum computing principles with machine learning techniques to solve problems that may be intractable using classical methods alone. This includes:
- Enhancing existing machine learning models with quantum speedup
- Designing hybrid algorithms that combine classical and quantum computation
- Leveraging quantum-native approaches for analyzing quantum data
FRIPL’s research in QML is focused on developing algorithms that can run on Fujitsu’s quantum simulators and hardware, with long-term potential for applications in optimization, language processing, and 3D data analysis.
Quantum Error Correction
Quantum Error Correction (QEC) is essential to ensure the reliability of quantum systems by addressing errors caused by quantum noise. Since quantum information cannot be copied directly due to the no-cloning theorem, QEC relies on distributing quantum states across multiple qubits and using syndrome measurements for error detection and correction.
FRIPL is researching the design and application of robust QEC codes that are critical for the transition to large-scale fault-tolerant quantum systems.
Early Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation and Beyond
Early FTQC refers to systems that use limited quantum resources and offer trade-offs between accuracy and resource usage. This regime enables algorithm development using partial error correction and smaller qubit counts.
In the longer term, full FTQC will rely on advanced QEC systems and access to large numbers of low-noise qubits. These systems will enable reliable implementation of powerful quantum algorithms for problems such as solving linear equations, database search, and cryptography.
FRIPL is working on incorporating FTQC modules into enterprise workflows to improve performance and scalability.
Join the Quantum research community at FRIPL
At Fujitsu Research of India, we are advancing the future of quantum computing through deep research and global collaboration. If you are passionate about quantum technologies, AI integration, and scientific innovation, FRIPL offers an opportunity to be part of meaningful projects with real-world impact.
Explore career opportunities, collaborate with world-class researchers, and contribute to Fujitsu’s mission of building a more connected, intelligent, and sustainable world through quantum research.
Meet our leadership

Krishnakumar Sabapathy
Krishnakumar Sabapathy is a quantum information scientist with over a decade of post-PhD research experience across academia and industry in India, Europe, and Canada. He specializes in building practical R&D solutions across the quantum technology stack, spanning quantum theory, algorithms, applications, and software.
Currently focused on enabling enterprise and research users to harness quantum hardware effectively, Krishnakumar also contributes to advancing hardware development through deep, application-driven insights. With a no hype, impact first approach, he brings a rare combination of theoretical depth and industry relevance, especially in areas like photonic quantum computing, fault tolerant architectures, and quantum communication. His mission is to drive meaningful progress in the emerging quantum ecosystem.
